What Is an APK File?
An APK file, short for “Android Package Kit,” is the standard file format used to install apps on Android devices. It contains every element an app needs to run—from code to graphics to configuration files. This compressed archive ensures the Android OS knows exactly how to install, launch, and manage an application.
Whether you’re a developer, tester, or curious Android user, understanding what an APK file is and how it works can unlock powerful customization and control over your Android experience.
What Are APK Files Used For?
APK files are the digital containers of Android apps. They enable users to install apps directly on their devices, bypassing official stores when needed. Google Play uses APKs behind the scenes to install apps, but due to Android’s open nature, users can also manually download APKs from third-party sources like APKMirror or APKPure.
This flexibility is useful for beta testing, sideloading region-locked apps, or accessing older app versions. However, this freedom also brings security concerns if the APK isn’t from a trusted source.
Key Components of an APK File
Every APK is a structured archive with essential parts that make up an Android app:
- AndroidManifest.xml: Declares the app’s package name, required permissions, and structure.
- classes.dex: Contains the compiled code in Dalvik bytecode, enabling Android to run the app.
- resources.arsc: Holds precompiled resources like UI strings, styles, and themes.
Additional folders like /res, /assets, /lib, and /META-INF/ hold everything from app graphics to native libraries and Structure of an APK File to validate the APK’s integrity.
How Does an APK Work?
An APK file operates by c into a format Android can interpret. When installed, the Android OS:
- Unpacks the APK, extracting code and assets.
- Reads the manifest for instructions on permissions and components.
- Places files in system directories and prepares them for execution.
- packaging app data using the Android Runtime (ART) or Dalvik.
This entire process ensures the app runs securely and integrates seamlessly with the device’s APIs, hardware, and system services.
How to Open and Download or transfer
To manually install an APK on your Android device:
- Enable “Install from Unknown Sources” in system settings.
- Download or transfer the APK file.
- Use a file manager to locate and tap the APK.
- Confirm the installation prompt.
- Once installed, open the app from your app drawer.
Manual installation gives you full control, but only proceed with verified APKs to avoid malware or device instability.
Though APK files offer flexibility, downloading from untrusted sources can be risky. Major risks include:
- Malware or viruses embedded in rogue APKs.
- Data theft through unauthorized permissions.
- Lack of automatic updates, leading to outdated or buggy apps.
Always be cautious and avoid installing APKs that demand excessive permissions, come from unknown publishers, or lack community reviews.
How to Ensure APK Files Are Safe
Here are best practices to ensure APK safety:
- Download only from trusted sources like APKMirror or the app’s official site.
- Use a reputable antivirus app to scan APKs.
- Carefully review requested permissions—a photo app doesn’t need access to contacts.
- Read user reviews on forums or APK hubs to check for known issues or malware.
Practicing APK hygiene is essential to keeping your device secure and performant.
How to Create an APK File
Using Android Studio, developers can build APKs in two main formats:
1. Debug APK
Used for testing purposes. To create:
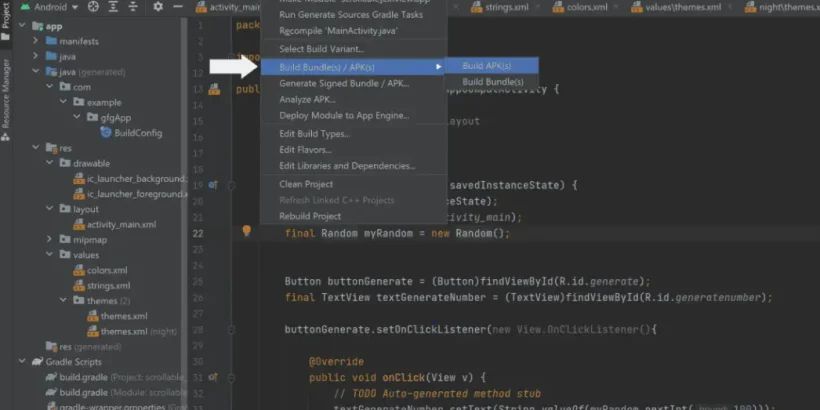
- Go to
Build > Build Bundle(s)/APK(s) > Build APK(s) - Useful for internal testing but not suitable for publishing.
2. Signed APK
Required for public release. Steps include:
- Generate Key Store credentials.
- Select
Build > Generate Signed Bundle / APK. - Complete required credentials to secure the file.
This signed APK is ready for upload to the Play Store, ensuring authenticity and security.
How to Test an APK File
Testing your APK before release is critical to ensure performance, compatibility, and a smooth user experience.
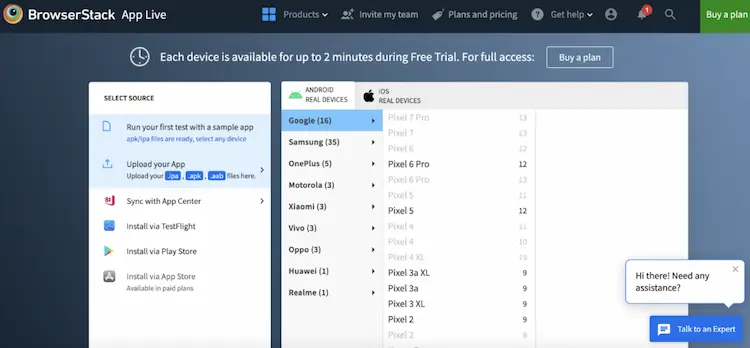
Option 1: Browser Stack App Live
BrowserStack allows remote testing on real Android devices. Here’s how:
- Upload your APK via the App-Live dashboard.
- Select your target Android device model.
- Test your app in real user conditions.
- Record sessions, debug with developer tools, and log issues.
With 3500+ devices, BrowserStack eliminates the need for physical device labs.
Option 2: Android Studio Emulator
Android Studio’s built-in emulator lets you:
- Run APKs on virtual devices.
- Use the Android Profiler to check performance.
- Simulate various Android versions.
While useful, emulators often suffer from limited accuracy, high RAM usage, and slower speeds compared to real devices.
Why Test APK Files on Browser Stack?
BrowserStack App Live provides:
- Real Device Cloud for authentic performance testing.
- Access to 15+ native features like GPS and localization.
- Dev tools for crash logs, console debugging, and UI inspection.
- Ability to simulate poor networks, screen rotation, and language changes.
This platform ensures that your APK performs flawlessly across the full Android ecosystem.
APK vs AAB: Which One Should You Use?
| Feature | APK | AAB (Android App Bundle) |
|---|---|---|
| File Size | Larger | Smaller and optimized |
| Distribution | Anywhere | Only via Google Play |
| Optimization | One-size-fits-all | Device-specific APKs |
| Installation | Direct | Indirect via Play Store |
| Usage | Sideloading, testing | Official app publishing |
While APKs are great for testing and direct installs, AABs are the future of Android app distribution through the Play Store.
How to Test APK Files on a PC
BrowserStack enables easy APK testing on desktops using a web browser. After uploading your file, you can:
- Test landscape vs. portrait views.
- Debug crashes and check logs.
- Change location or language settings.
- Throttle network speeds to test on poor connections.
All without touching a physical Android device.
Conclusion
An APK (Android Package Kit) is a powerful tool that drives the Android app ecosystem. It packages all the code, assets, and metadata needed to install and run apps. While APKs offer unparalleled flexibility, they also carry security risks if not handled properly.
If you’re a developer or tester, testing APK files on real devices using platforms like BrowserStack ensures your app works seamlessly under real-world conditions—no physical lab needed.